As ecommerce experiences demand higher performance, richer UX, and omnichannel delivery, traditional Magento storefronts begin to show limitations. This has driven the rise of headless Magento, where the frontend is completely decoupled and powered by modern frameworks like React and Next.js.
This guide explains how Magento Next.js implementations work, the architecture behind them, and how developers can build scalable headless Magento storefronts.
“Magento doesn’t become slower — monolithic frontends do.”
What Is Headless Magento?
Headless Magento is an architecture where:
- Magento acts as the commerce backend only
- Frontend is built separately using React or Next.js
- All communication happens via APIs
- Magento themes are bypassed entirely
Magento handles:
- Products
- Pricing
- Inventory
- Cart
- Checkout
- Customers
- Promotions
The frontend consumes Magento through APIs.
Why Use Headless Magento?
Headless Magento is ideal for:
- High-traffic ecommerce stores
- Custom UX requirements
- Progressive Web Apps (PWA)
- Omnichannel commerce
- Enterprise integrations
“Headless Magento turns Magento into a commerce engine — not a website.”
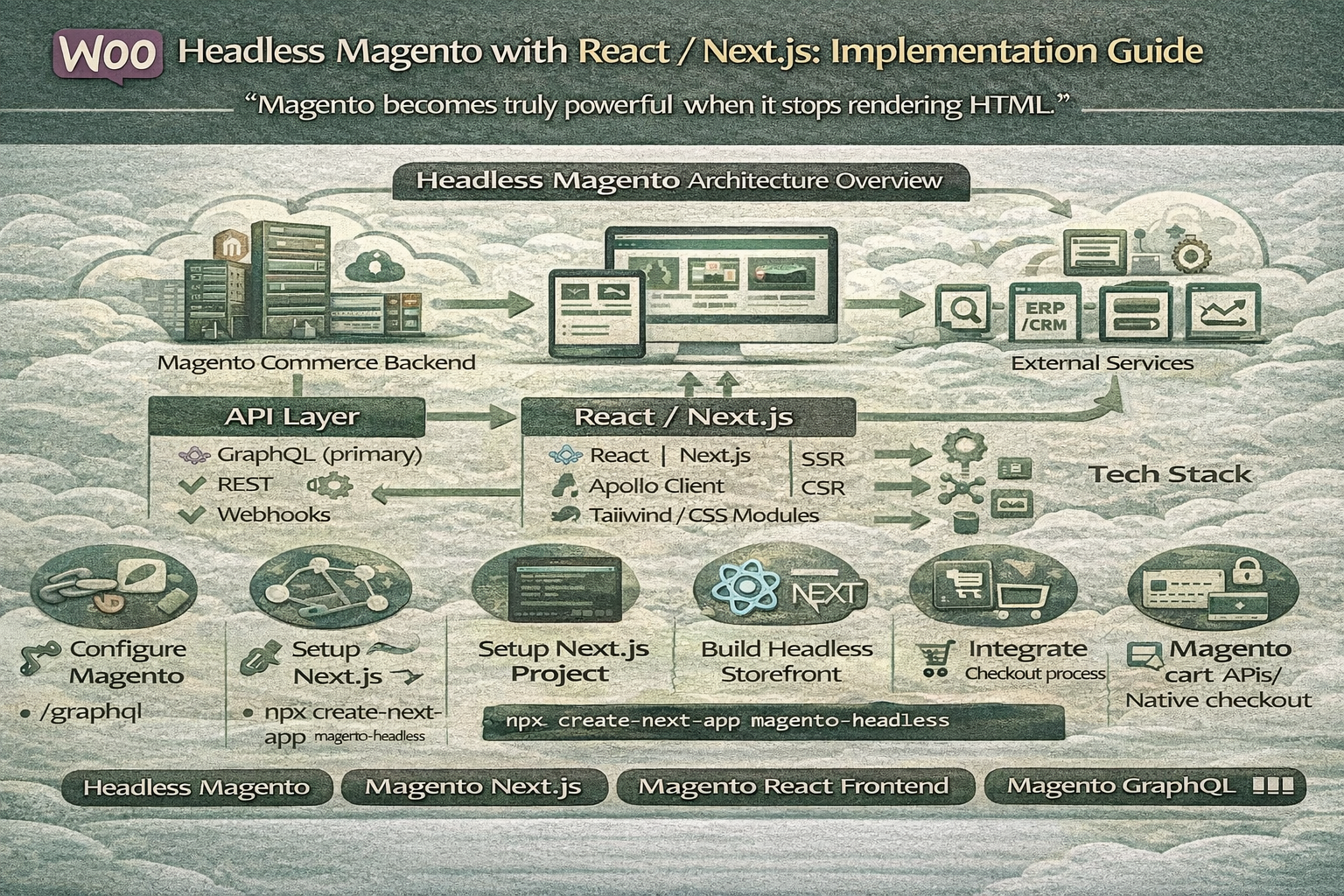
Headless Magento Architecture Overview
Core Layers
- Magento Backend
- Adobe Commerce
- Catalog, pricing, checkout logic
- Business rules
- API Layer
- GraphQL (primary)
- REST (secondary)
- Webhooks
- Frontend Layer
- React or Next.js
- Server-side rendering (SSR)
- Static generation (SSG)
- External Services
- CMS
- Search (Algolia)
- Payment gateways
- Analytics
Why GraphQL Is Mandatory for Headless Magento
Magento’s GraphQL API is built specifically for headless use cases.
Benefits
- Query exactly what you need
- Reduce over-fetching
- Faster frontend performance
- Optimized for React rendering
Magento strongly recommends GraphQL for all headless storefronts.
“If you’re building headless Magento without GraphQL — you’re doing it wrong.”
Magento + Next.js Architecture Flow
- User loads Next.js storefront
- Next.js requests data via Magento GraphQL
- Magento processes commerce logic
- Data returned to frontend
- React components render UI
This allows:
- SSR for SEO
- ISR for performance
- CSR for dynamic interactions
Tech Stack for Headless Magento
Backend
- Magento 2.4+
- Adobe Commerce
- GraphQL enabled
- Redis
- Elasticsearch / OpenSearch
Frontend
- Next.js (recommended)
- React
- Apollo Client or urql
- Tailwind / CSS Modules
Infrastructure
- CDN
- Edge caching
- API gateway
- Varnish (backend only)
Step-by-Step Implementation Guide
Step 1: Prepare Magento Backend
Enable GraphQL and configure:
- Store views
- Currencies
- Tax rules
- Inventory sources
- Product attributes
Ensure GraphQL endpoints are publicly accessible.
Step 2: Configure Magento GraphQL
Test endpoints:
/graphql
Example query:
query {
products(search: "shirt") {
items {
name
sku
price_range {
minimum_price {
final_price {
value
currency
}
}
}
}
}
}
This confirms Magento API readiness.
Step 3: Setup Next.js Project
Create project:
npx create-next-app magento-headless
Install dependencies:
npm install @apollo/client graphql
Configure Apollo Client to connect Magento GraphQL endpoint.
Step 4: Build Product & Category Pages
- Use dynamic routing
- Fetch data using GraphQL
- Implement ISR for performance
- Use SSR for SEO pages
Next.js supports:
getServerSidePropsgetStaticPropsrevalidate
Step 5: Cart & Checkout Integration
Options:
- Magento native checkout via API
- Embedded checkout
- Redirect-based checkout
- Custom checkout UI
Magento checkout is complex and should be implemented carefully.
“Checkout is where most headless Magento projects fail — plan it early.”
Step 6: Authentication & Customer Accounts
Use:
- Magento customer tokens
- Secure cookie storage
- Session persistence
- Refresh token handling
Avoid exposing admin APIs.
Step 7: Performance Optimization
- Cache GraphQL queries
- Use CDN edge caching
- Implement ISR
- Optimize images
- Reduce GraphQL payload size
SEO in Headless Magento
Next.js provides:
- Server-side rendering
- Meta tags
- Structured data
- Clean URLs
SEO must be implemented manually — unlike Magento themes.
“Headless improves SEO only when SSR is done correctly.”
Common Challenges in Headless Magento
- Checkout complexity
- GraphQL learning curve
- Higher development cost
- State management
- SEO implementation
Headless Magento is powerful — but not beginner-friendly.
When Headless Magento Makes Sense
Choose headless Magento if:
- You run enterprise-scale ecommerce
- You need complex pricing rules
- You have large catalogs
- You require global scalability
- You have an experienced dev team
Magento PWA Studio vs Next.js
| Feature | PWA Studio | Next.js |
|---|---|---|
| Magento native | Yes | No |
| Flexibility | Limited | High |
| Performance | Good | Excellent |
| Ecosystem | Magento only | Massive |
| SEO | Moderate | Excellent |
Next.js is increasingly preferred for enterprise storefronts.
Conclusion
Headless Magento with React / Next.js provides unmatched flexibility, performance, and scalability for enterprise ecommerce platforms.
By decoupling the frontend and using Magento as a commerce engine, businesses gain complete control over UX, integrations, and performance.
“Magento becomes truly powerful when it stops rendering HTML.”