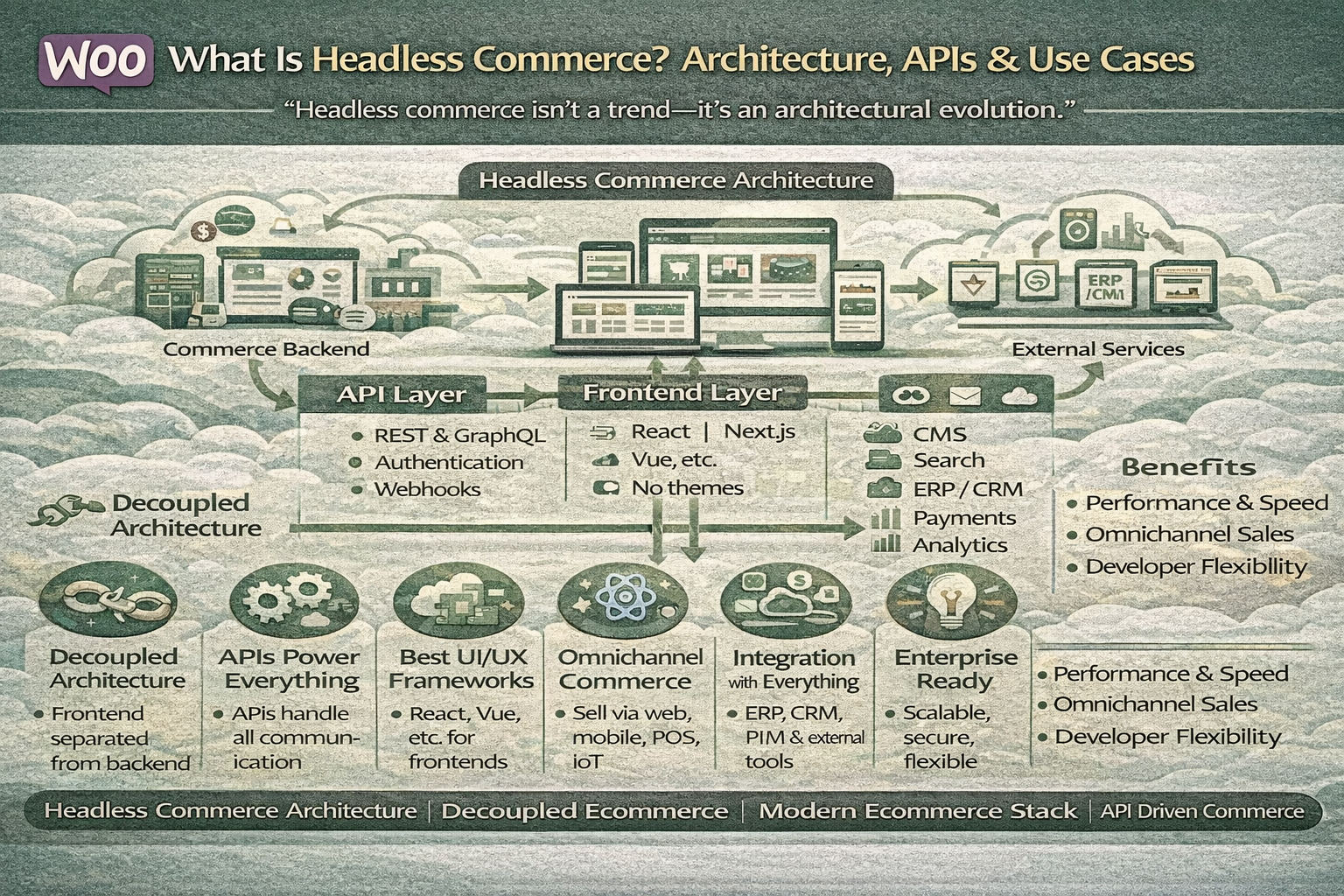
Traditional ecommerce platforms tightly couple the frontend and backend. While this approach works for basic stores, it becomes a limitation when brands need faster experiences, omnichannel delivery, and flexible integrations.
This is where headless commerce changes everything.
In this guide, we’ll break down headless commerce architecture, explain how APIs power it, and explore real-world use cases.
“Headless commerce isn’t about removing the frontend — it’s about freeing it.”
What Is Headless Commerce?
Headless commerce is an ecommerce architecture where:
- Frontend (presentation layer) is decoupled
- Backend (commerce engine) operates independently
- Communication happens via APIs
Instead of a single monolithic system, headless commerce separates concerns — allowing developers to build any frontend while using a centralized commerce backend.
Traditional vs Headless Commerce
Traditional (Monolithic)
- Frontend and backend tightly coupled
- Limited customization
- Slower innovation
- Theme-based rendering
Headless Commerce
- Frontend and backend separated
- API-driven communication
- Faster frontend performance
- Omnichannel flexibility
“Monolithic platforms control how you build — headless lets you decide.”
Headless Commerce Architecture Explained
At its core, headless commerce architecture consists of multiple independent layers.
1. Commerce Backend
Handles:
- Products
- Pricing
- Inventory
- Orders
- Customers
- Payments
- Promotions
Examples:
- Shopify (Storefront API)
- Magento / Adobe Commerce
- BigCommerce
- Commercetools
2. API Layer
APIs act as the communication bridge.
Common APIs include:
- REST APIs
- GraphQL APIs
- Webhooks
- Authentication services
APIs expose commerce functionality to any frontend or channel.
3. Frontend Layer (Head)
Built independently using modern frameworks:
- React
- Next.js
- Nuxt
- Vue
- Svelte
This frontend consumes APIs instead of rendering server-side templates.
4. External Services
Headless systems often integrate:
- CMS (Contentful, Sanity, Strapi)
- Search (Algolia)
- Payment gateways
- Analytics tools
- ERP / CRM systems
Each service operates independently.
Headless Commerce Data Flow
- User interacts with frontend
- Frontend sends API request
- Backend processes logic
- API returns data
- Frontend renders UI
This architecture enables speed, flexibility, and scalability.
“APIs become the backbone of the entire commerce experience.”
Why APIs Are Critical in Headless Commerce
APIs enable:
- Channel independence
- Faster frontend development
- Reusable commerce logic
- Microservices architecture
- Real-time integrations
GraphQL is commonly preferred because it reduces over-fetching and improves performance.
Key Benefits of Headless Commerce
1. Performance & Speed
- Faster page loads
- Better Core Web Vitals
- Optimized frontend rendering
2. Omnichannel Commerce
- Web
- Mobile apps
- POS
- Marketplaces
- IoT devices
3. Developer Freedom
- Any frontend framework
- Custom UX
- No theme limitations
4. Scalability
- Independent scaling of frontend and backend
- Better handling of traffic spikes
“Headless commerce scales systems — not just stores.”
Common Headless Commerce Use Cases
1. High-Performance Ecommerce Stores
Brands needing sub-second page loads and SEO optimization.
2. Omnichannel Retail
Selling across web, mobile apps, kiosks, and marketplaces.
3. Custom UX & UI Experiences
Unique customer journeys not possible with themes.
4. Global Commerce
Multi-region storefronts with localized frontends.
5. Enterprise Integrations
ERP, OMS, CRM, PIM integrations via APIs.
Headless Commerce vs Traditional Commerce
| Feature | Traditional | Headless |
|---|---|---|
| Frontend flexibility | Limited | Unlimited |
| Performance | Moderate | High |
| Scalability | Vertical | Horizontal |
| Omnichannel | Difficult | Native |
| Development speed | Slower | Faster |
Challenges of Headless Commerce
While powerful, headless comes with tradeoffs:
- Higher development cost
- Requires strong technical team
- More complex architecture
- SEO requires proper implementation
“Headless commerce offers freedom — but freedom requires discipline.”
When Should You Use Headless Commerce?
Headless is ideal when:
- You need high performance
- You plan omnichannel expansion
- UX customization is critical
- You have development resources
- Your store is scaling rapidly
For small stores, traditional platforms may still be sufficient.
Popular Headless Commerce Platforms
- Shopify Headless (Hydrogen, Storefront API)
- BigCommerce Headless
- Magento Headless
- Commercetools
- Saleor
- Medusa
Conclusion
Headless commerce represents the future of scalable ecommerce. By separating frontend and backend and relying on APIs, businesses gain unmatched flexibility, speed, and control.
Understanding headless commerce architecture is essential for building modern, future-ready ecommerce platforms.
“Headless commerce isn’t a trend — it’s an architectural evolution.”